AL-Kurdhani JMH, Huajun Wang and Elrasheed Elhaj
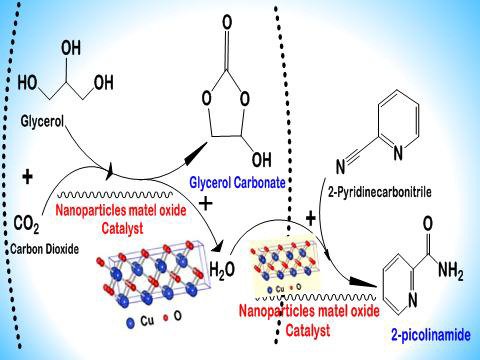
Four types of metal oxide nanoparticle catalysts (La2O3, NiO, CuO, and Co3O4) are prepared by precipitation method and used for the synthesis of glycerol carbonate from the direct carbonylation of glycerol and carbon dioxide in the presence of dehydrating agent and solvent. The effects of calcination temperatures, dehydrating agents, and reaction parameters on the conversion of glycerol and yield of glycerol carbonate are investigated. XRD, FT-IR, SEM, BET, CO2-TPD, H2-TPR and ICP-MS are used for the characterization of the prepared catalysts. It is found that the efficient catalyst for the carbonylation of glycerol should have not only large amount of basic sites and surface area, but also high redox ability and oxygen vacancy. CuO with calcination at 400°C exhibits higher catalytic activity and the best dehydrating agent is 2-Cyanopyridine. The active site of CuO catalyst may be crystal face (111). Under condition of 150°C, 4 MPa, 5 h, the glycerol carbonate yield can reach about 40%. The catalyst can be reused five times with little loss of activity and can be easily regenerated by calcination at 400°C.
ఈ కథనాన్ని భాగస్వామ్యం చేయండి